|
Blood analyses : urea and creatinine levels
are high. Clairances are abnormal.
Before kidney damage urinary tract hypertension can
be detected by :
1. Intravenous urography 2.Isotopic
nephrogram 3.
Use of scintiscanner
A
B
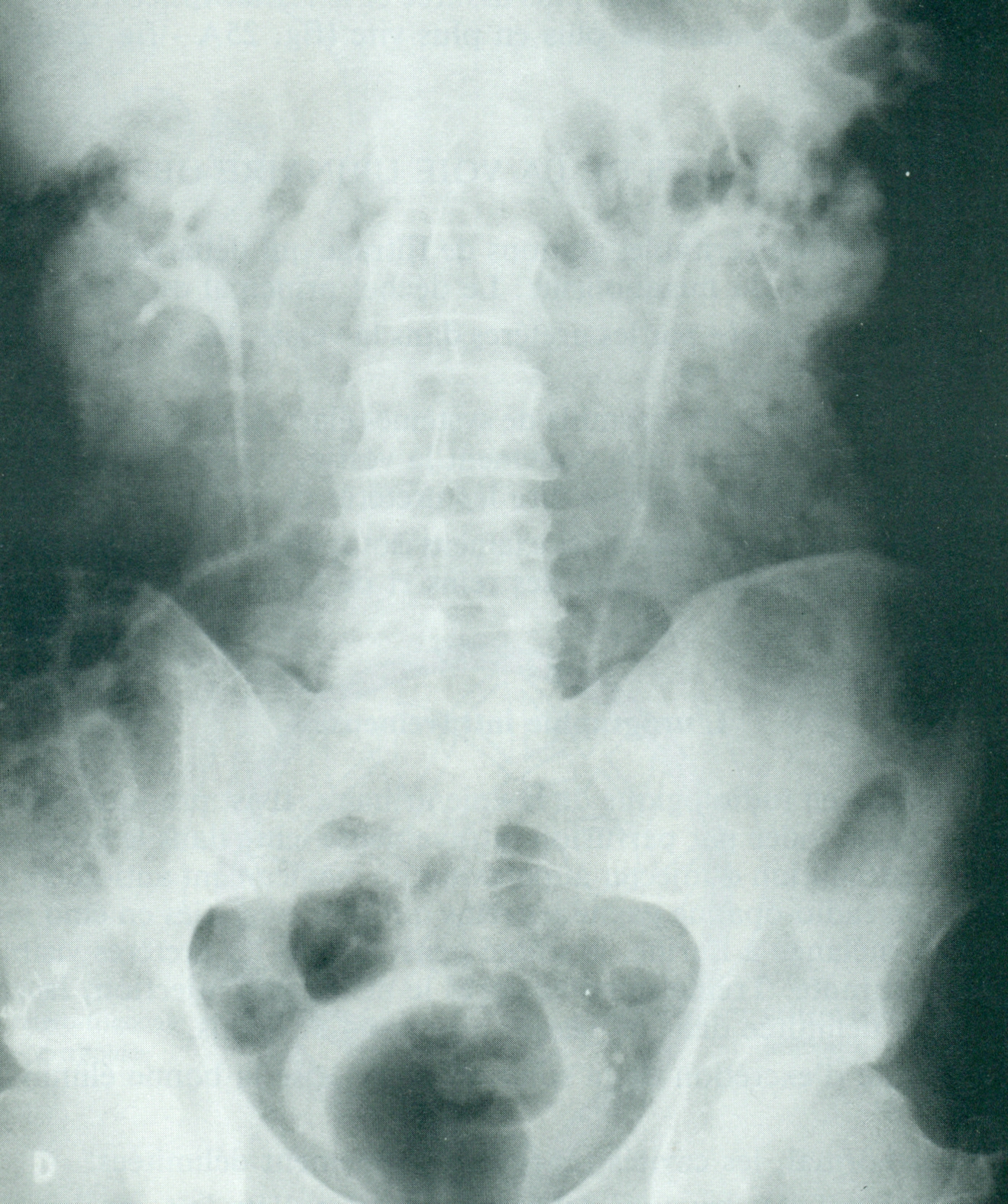
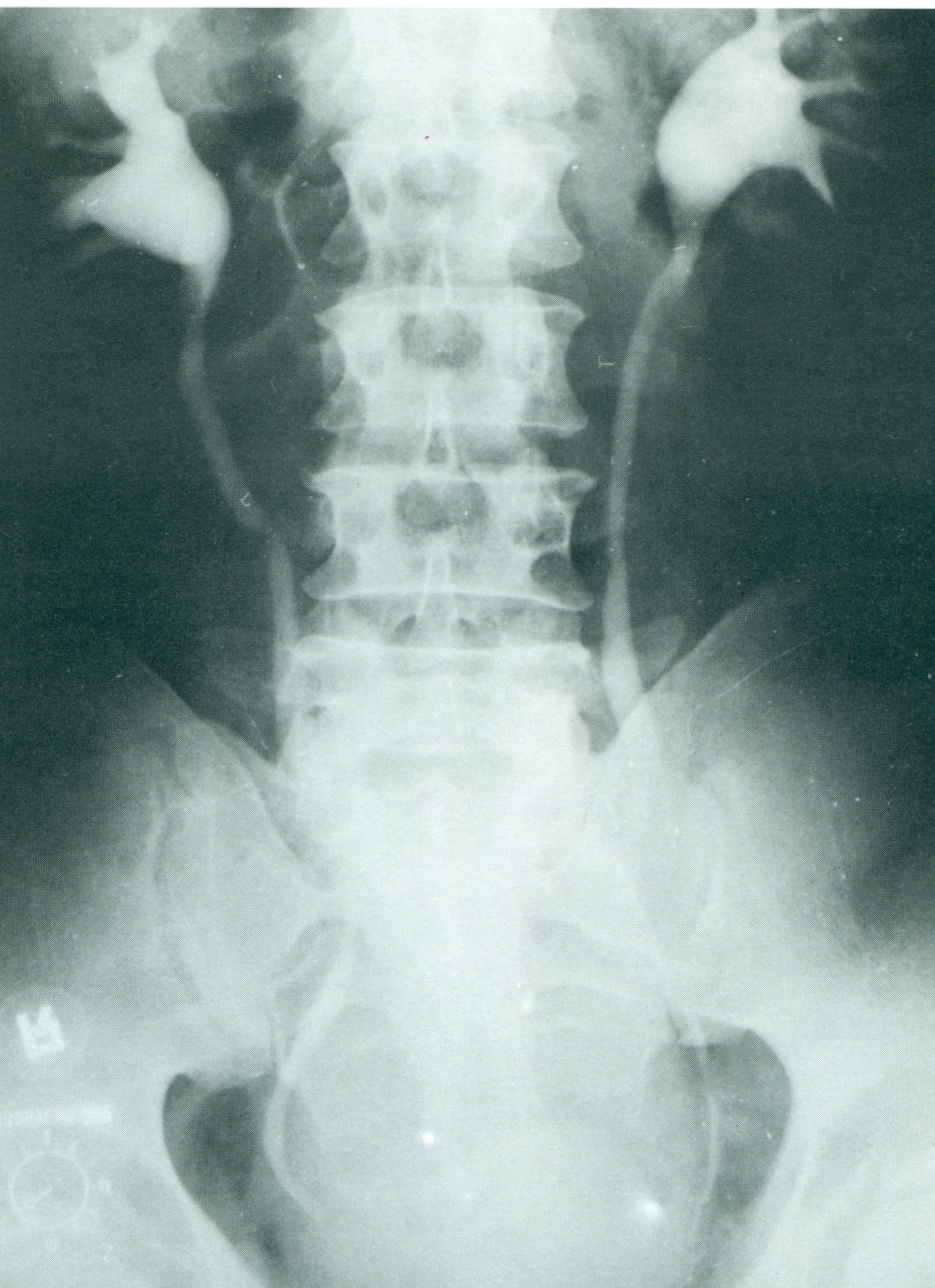
A. Normal
urography. Ureters are not shown on their entire
lenght..
B. Intravenous
urography. Hypertension of urinary tract. Ureters
are shown on their entire lenght .
C
D
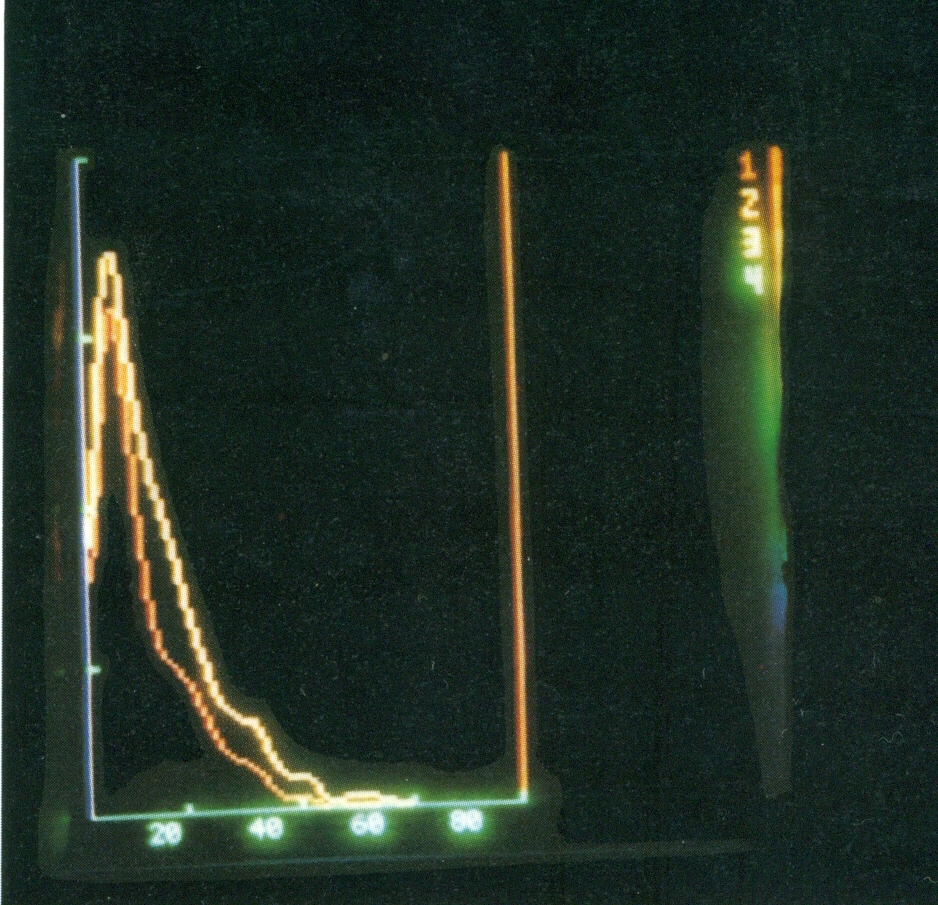
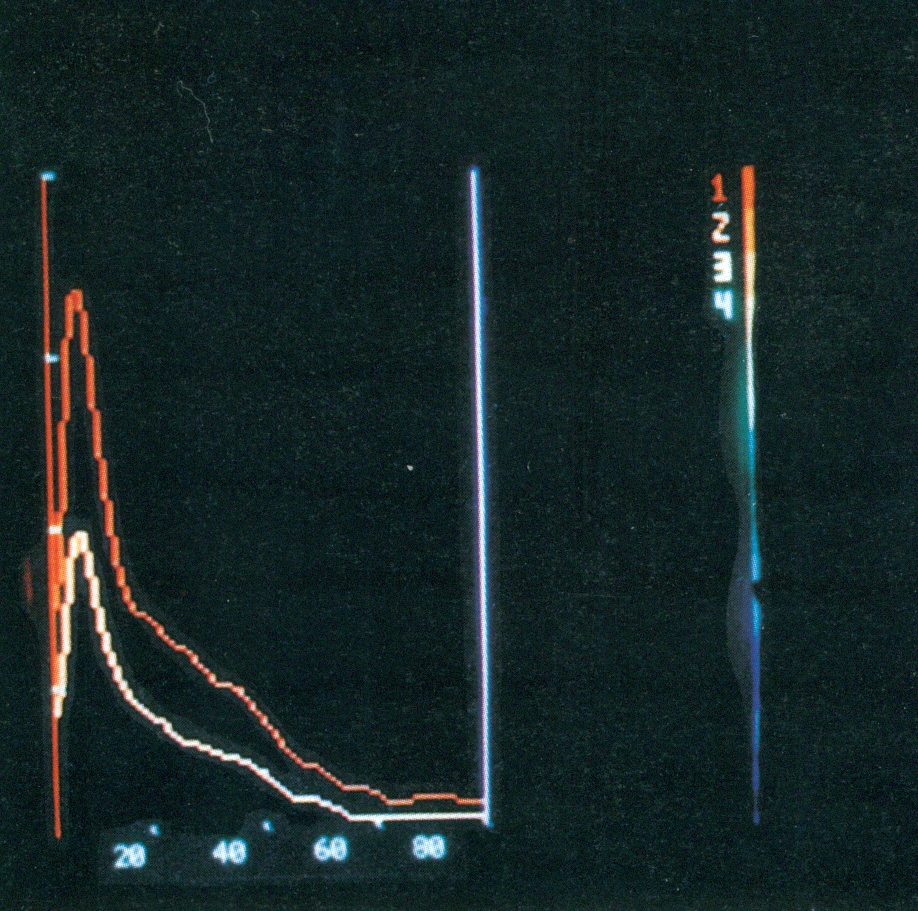
C. Normal
isotopic nephrogram. Quick elimination of both
kidneys.
D. Abnormal
isotopic nephrogram. Low elimination of both kidneys.
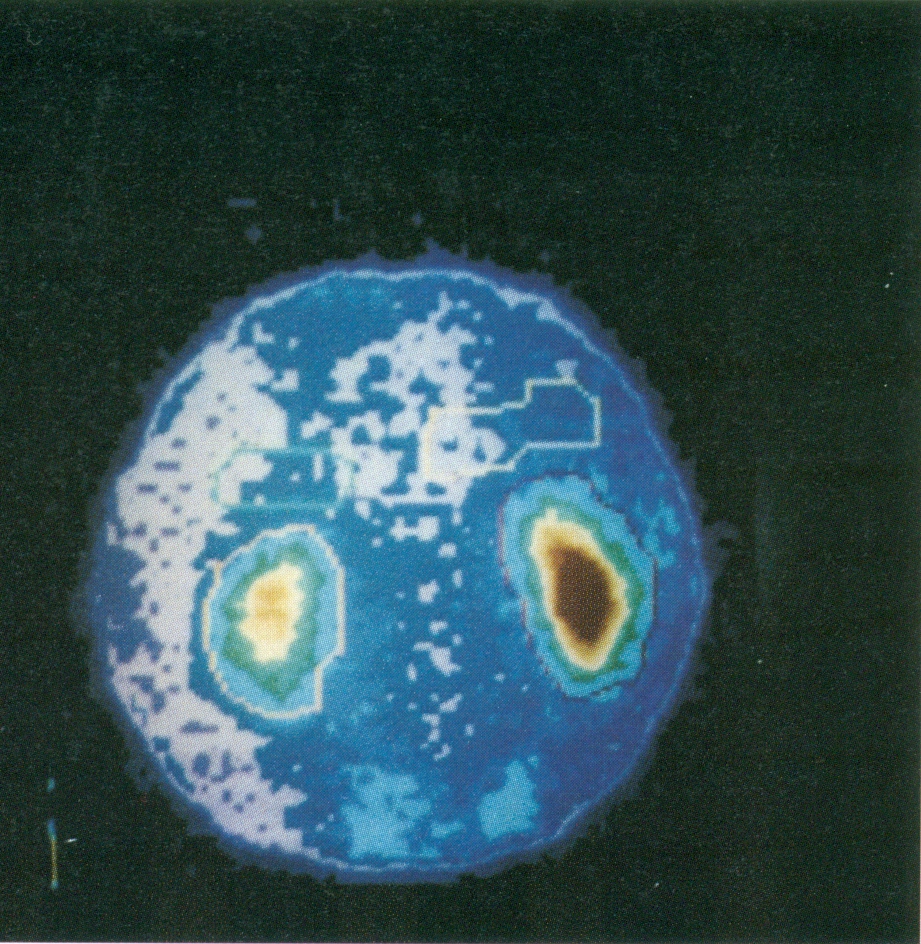
E
E. Scintiscanner
of kidneys. Left: poor kidney captation. Right:
normal captation (in
red).
Bladder neck
obstacle:
when urinary tract hypertension occurs (B and D),
to avoid kidney damage (E)
An endoscopic
resection of
bladder neck is necessary
|